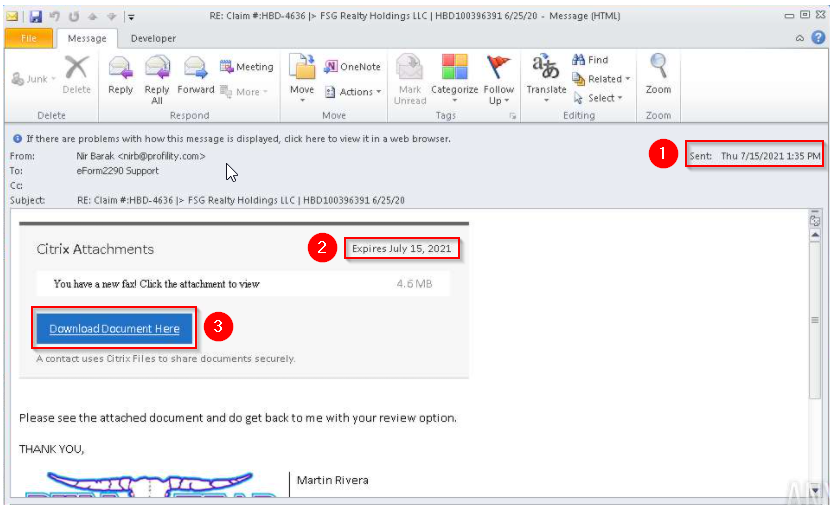
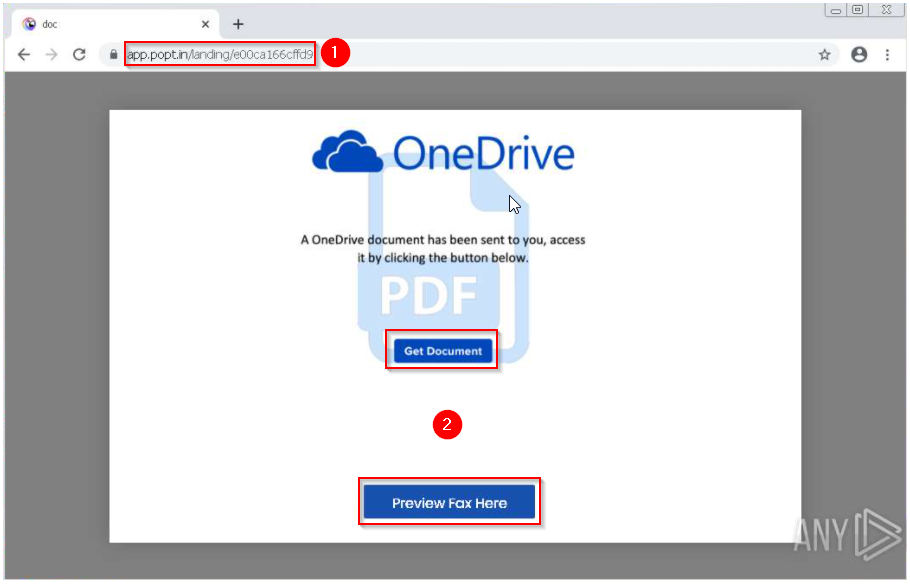
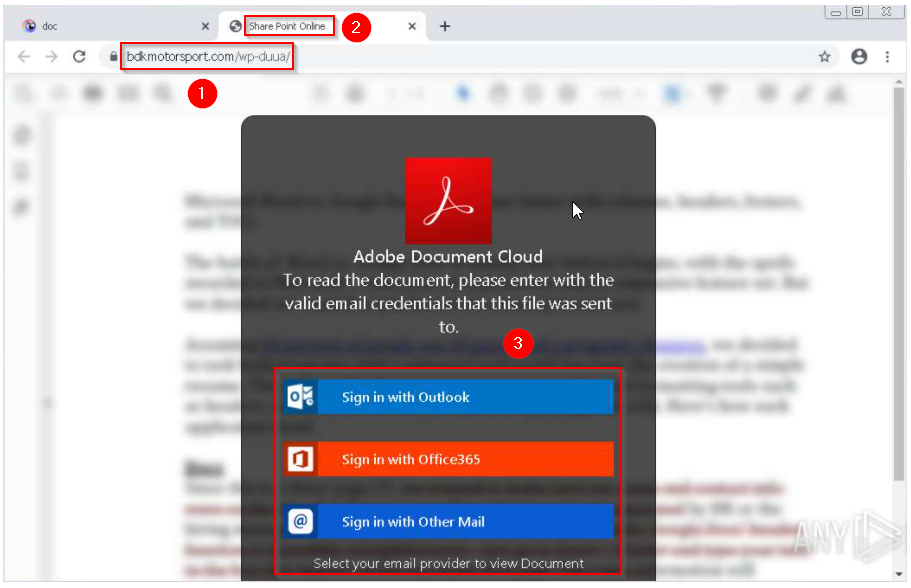
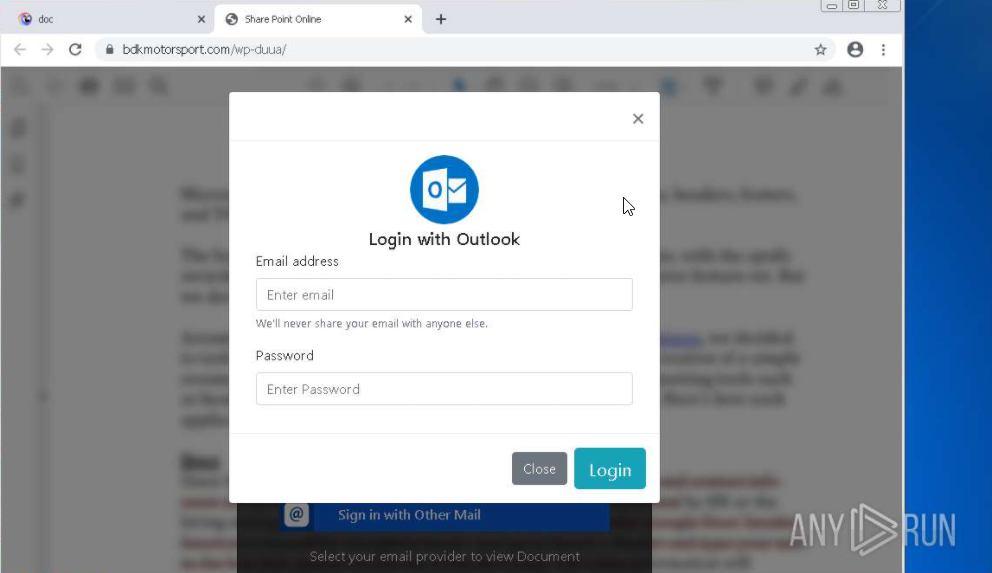
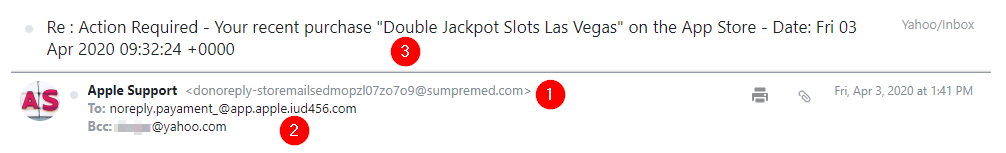
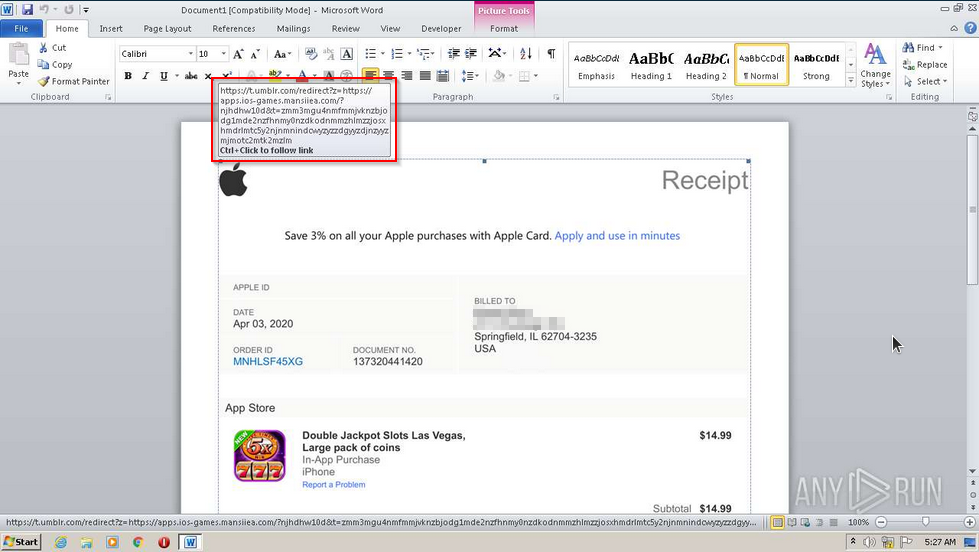
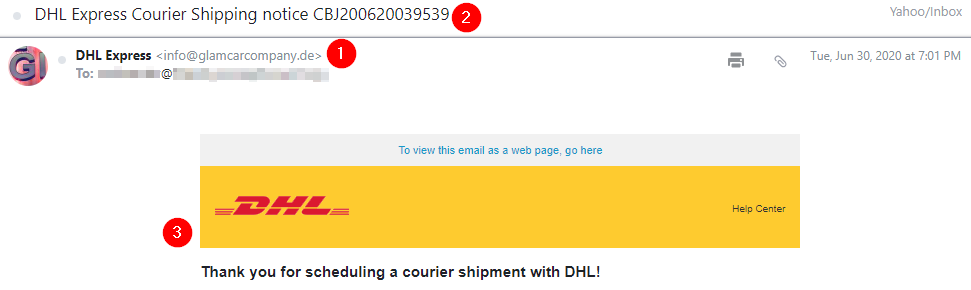
Now that we covered the basics concerning emails in Phishing Emails 1, let’s dive right into actual phishing email samples.
Each email sample showcased in this room will demonstrate different tactics used to make the phishing emails look legitimate. The more convincing the phishing email appears, the higher the chances the recipient will click on a malicious link, download and execute the malicious file, or even send the prince of some country a wire transfer.
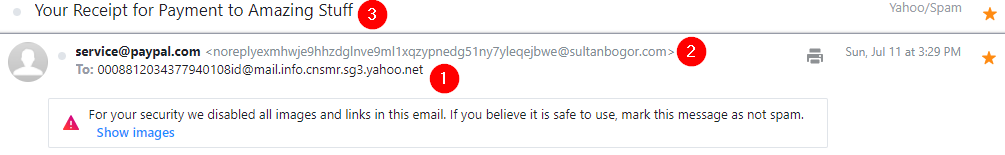
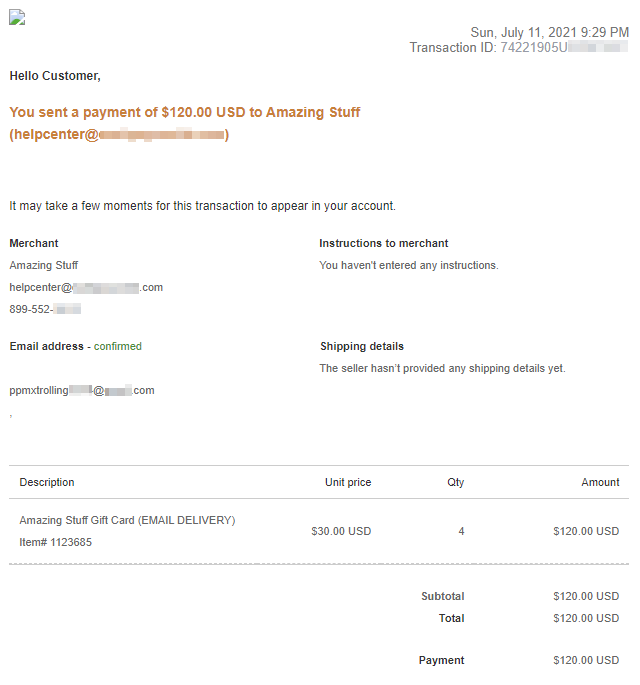
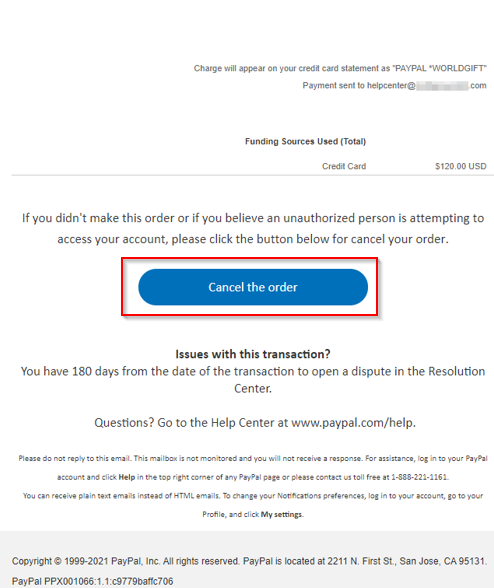
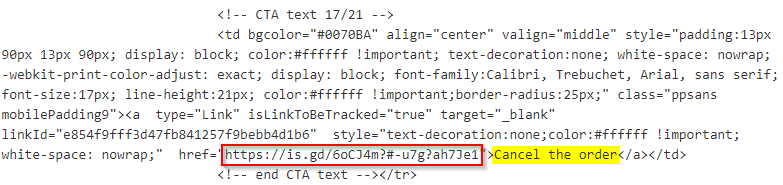
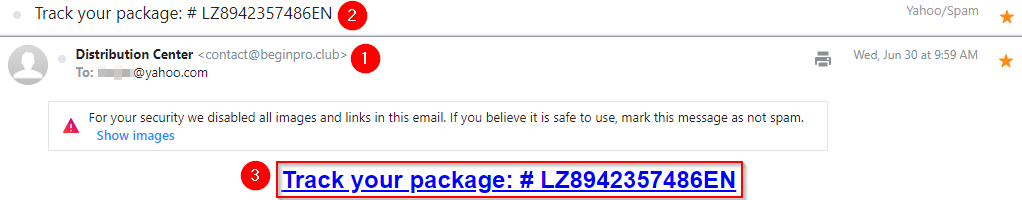
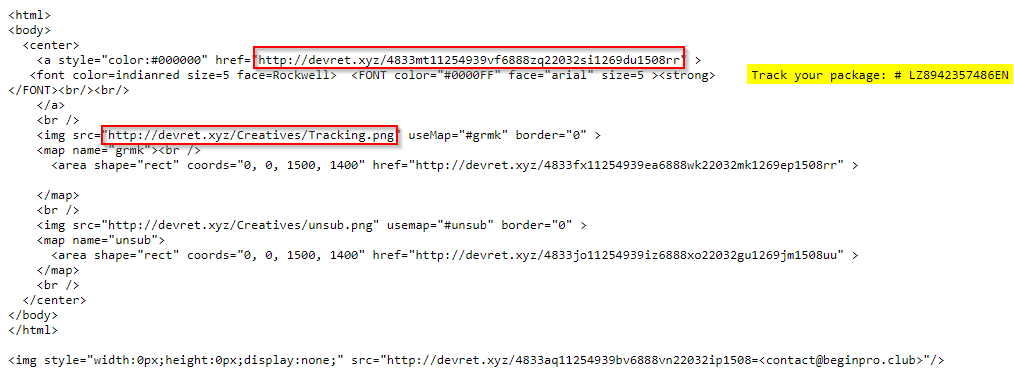
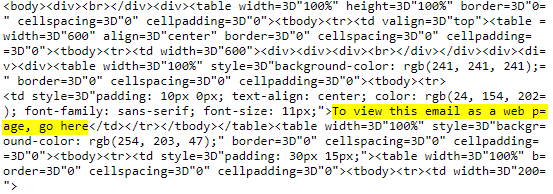
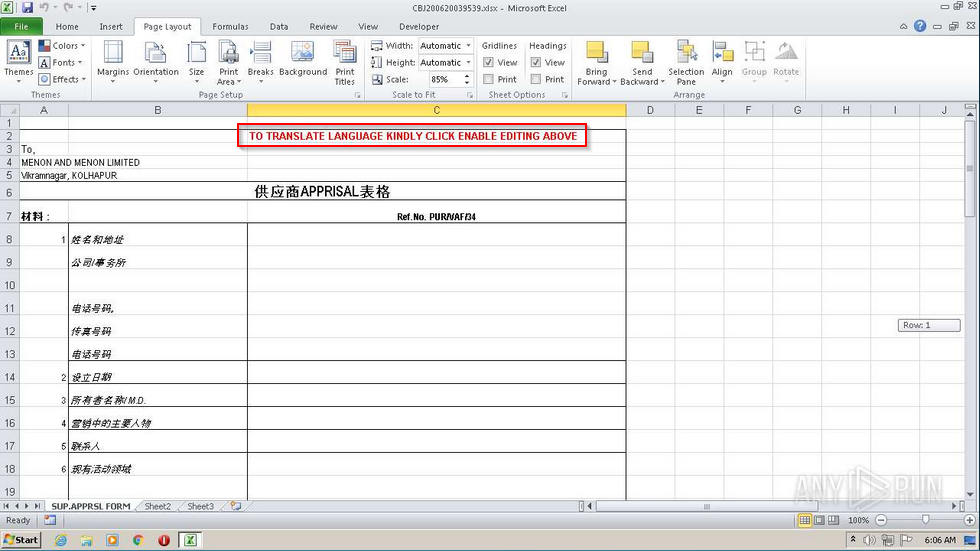
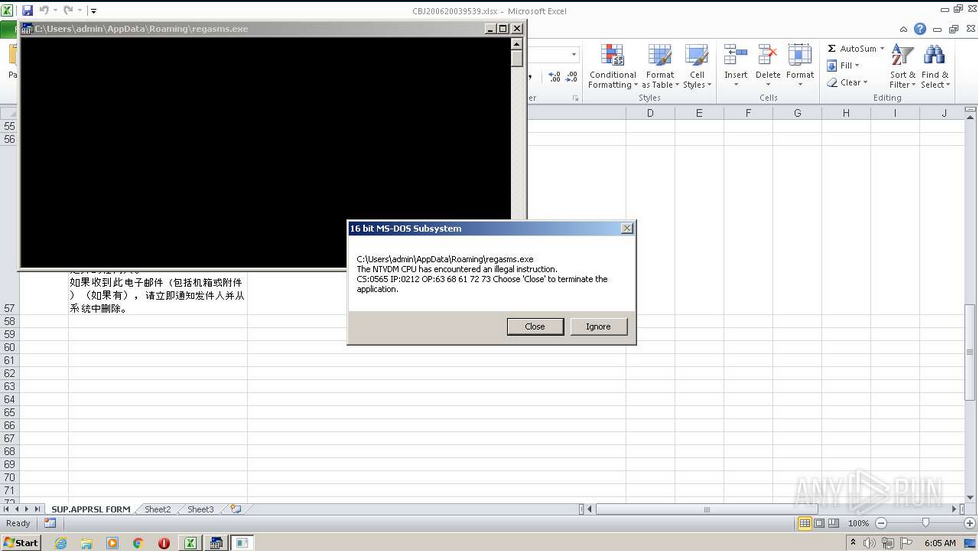
Warning: The samples throughout this room contain information from actual spam and/or phishing emails. Proceed with caution if you attempt to interact with any IP, domain, attachment, etc.
Answer the questions below
Read the above.
No answer need